APP development: React Native simplifies
8 min read
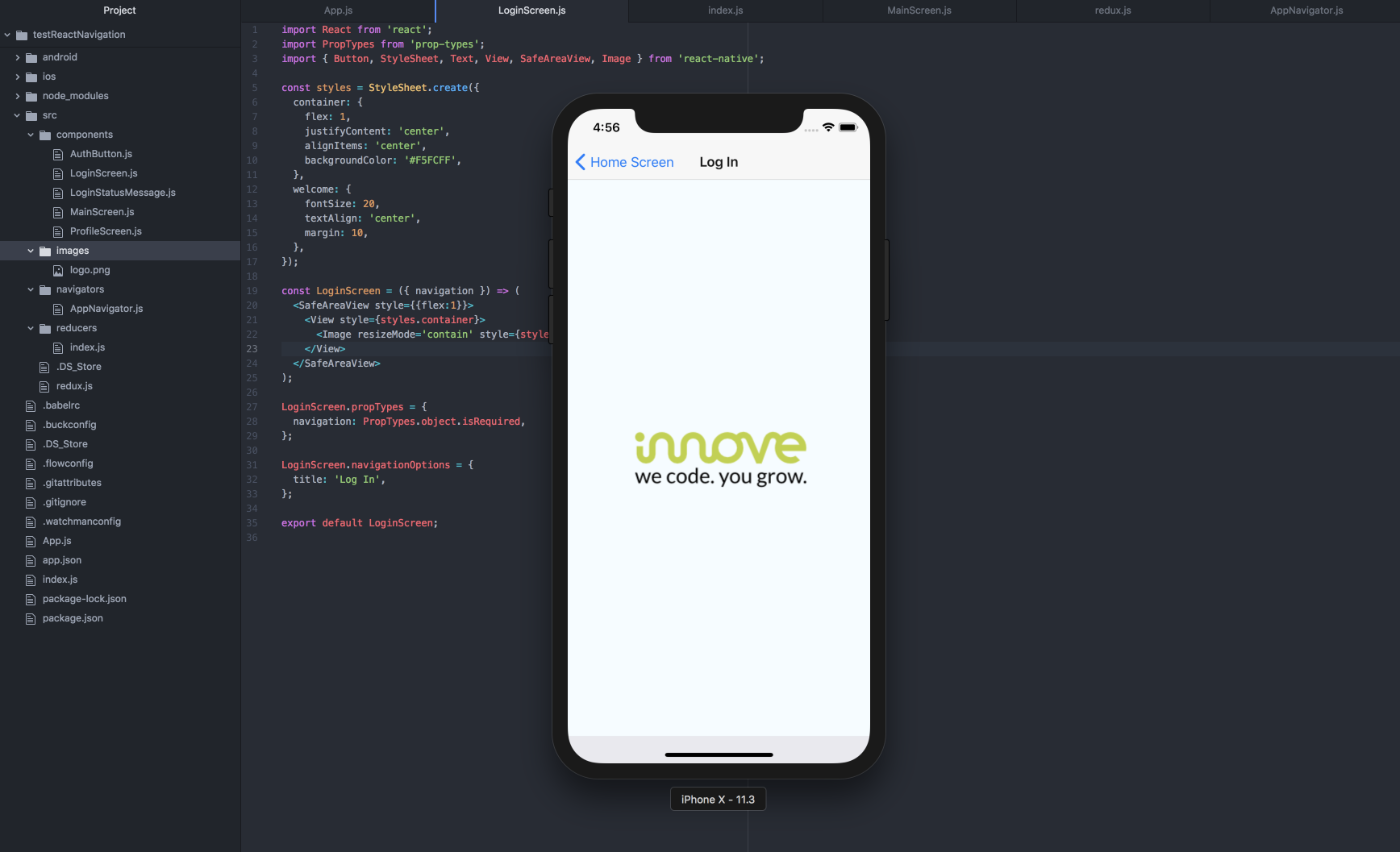
React Native is a software that simplify APP development reducing complications and costs as well as easing some matters.
Software for the APP development are in fact a lot and respond to different needs.
The basic idea is to take the most shared and standard part of each operating system, then the browser, and build on an application that behaves and displays more or less in the same way. More or less, because as we all know, even if huge steps have been taken, every browser has its own differences and the results must be verified.
Cordova, in short, allows you to create a web application using html / css / javascript and to make it run in a browser in the device in a "transparent" way for the user. In order to access the hardware features of the device, such as the camera or the GPS, there must be libraries, written in the specific language of the device, and which "speak" in a common way to the web application.
The main problem of this solution is the performance and the response speed of the UI, much improved by the increase in power of mobile devices, but which remains constrained by the bottleneck of the render of the browser page.
What is React? React is a javascript framework created by Facebook to improve the development and performance of the UI of its social network. The main objective was to minimize the browser rendering phases by creating a DOM parallel to the real one and trying to optimize the changes to be made.
We try to make a small example: at the click of a button an image is added to the DOM, checks are carried out, it is decided that the user does not have to see and remove it. In this operation we would have carried out two page renderings, one for each change, and then returned to the initial situation. Using React instead the operation of addition and removal remains only at the level of virtual DOM, since in the end the real DOM has not changed, no rendering is done.
The React Native website deceptively recites "Build native mobile apps using JavaScript and React", we try to understand why and how a step is taken further than Cordova.
Basic React Native can be used, being in Javascript, within a Cordova application by making the improvements we have just illustrated. In React Native, the UI is separated, maintaining the programming part in Javascript and a library system very similar to Cordova.
Starting from React's JSX template system, React Native creates the interface using native components of operating systems with improved performance and a smoother user experience in using the device. The applications are therefore not really "native" but try to emulate as much as possible the user interface and experience. The most interesting aspect compared to Xamarin is therefore that with React Native it is possible to reuse a lot more code and knowledge within different projects and to use a much more open ecosystem.
Although not technologically superior, React Native has had for these reasons a very rapid development and today has perhaps the most active and exciting ecosystem in the landscape.
Software for the APP development are in fact a lot and respond to different needs.
- Each operating system (Android, iOS, Windows) for smartphones is developed using its own programming language and tools.
- Developing an app for different systems would therefore require different teams for initial development, problem correction and maintenance over time. If you look back, many applications were born for a single operating system and could remain "exclusive" for years.
- Having different teams, in addition to raising costs, complicates all phases, a feature can arrive months before on one side and a bug being there only in a specific operating system.
CORDOVA
One of the first to give an interesting answer, still very used, is Cordova , which is based on PhoneGap (purchased a few years ago by Adobe).The basic idea is to take the most shared and standard part of each operating system, then the browser, and build on an application that behaves and displays more or less in the same way. More or less, because as we all know, even if huge steps have been taken, every browser has its own differences and the results must be verified.
Cordova, in short, allows you to create a web application using html / css / javascript and to make it run in a browser in the device in a "transparent" way for the user. In order to access the hardware features of the device, such as the camera or the GPS, there must be libraries, written in the specific language of the device, and which "speak" in a common way to the web application.
The main problem of this solution is the performance and the response speed of the UI, much improved by the increase in power of mobile devices, but which remains constrained by the bottleneck of the render of the browser page.
- https://phonegap.com/app/
XAMARIN
Another approach is used by Xamarin , born as a separate company / project and bought and integrated completely by Microsoft. In this case we start from a code written in C# which is compiled and interpreted by the "heart" of Xamarin which, based on the operating system, interfaces to the device. This approach certainly allows us to have higher performances but closes the development of the application in a very high enclosure. All the written code will be difficult to reuse in external projects and we need a development team with very specific knowledges that is difficult to spend in other fields. The ideal target is therefore a well-structured company, with a clear project to be developed probably internally. The list of Xamarin users can clarify the concept.REACT NATIVE
To talk about React Native we need to make a small digression on React .What is React? React is a javascript framework created by Facebook to improve the development and performance of the UI of its social network. The main objective was to minimize the browser rendering phases by creating a DOM parallel to the real one and trying to optimize the changes to be made.
We try to make a small example: at the click of a button an image is added to the DOM, checks are carried out, it is decided that the user does not have to see and remove it. In this operation we would have carried out two page renderings, one for each change, and then returned to the initial situation. Using React instead the operation of addition and removal remains only at the level of virtual DOM, since in the end the real DOM has not changed, no rendering is done.
The React Native website deceptively recites "Build native mobile apps using JavaScript and React", we try to understand why and how a step is taken further than Cordova.
Basic React Native can be used, being in Javascript, within a Cordova application by making the improvements we have just illustrated. In React Native, the UI is separated, maintaining the programming part in Javascript and a library system very similar to Cordova.
Starting from React's JSX template system, React Native creates the interface using native components of operating systems with improved performance and a smoother user experience in using the device. The applications are therefore not really "native" but try to emulate as much as possible the user interface and experience. The most interesting aspect compared to Xamarin is therefore that with React Native it is possible to reuse a lot more code and knowledge within different projects and to use a much more open ecosystem.
Although not technologically superior, React Native has had for these reasons a very rapid development and today has perhaps the most active and exciting ecosystem in the landscape.
Within the same category
Il nuovo ITSM in breve
8 min read
